Have you ever seen a small box on the side of your house with numbers or a screen on it? That’s an electric meter.
| Photo Credit: Pexels
You must have been asked to switch off lights and fans while leaving a room and lectured about how the electricity bill will skyrocket. Have you ever wondered how the electricity meter or the watt-hour meter works? How do we understand how much electricity we have consumed and how much to pay? Let’s dive into the science behind this important adulting skill!
Before we go into the physics behind an electric meter, let’s understand what an electric meter is. An electricity meter is a device that keeps track of how much electricity your home uses. It works by measuring the flow of electricity through your house and converting it into a number that shows how much energy you’ve used. This number is then used to calculate the cost of electricity used by multiplying it by the unit cost of electricity in your region.
Inside an electric meter
Have you ever seen a small box on the side of your house with numbers or a screen on it? That’s an electric meter. Electricity flows into your house through wires. The meter is placed right where the electricity enters the house.
As the electricity flows through the meter, it records the amount of electricity used in something called kilowatt-hours (kWh). Kilowatt-hours is the unit in which the energy used is calculated.
The process
When electricity travels from the power lines into your home, it first goes through the electric meter. The meter is like a gate that checks how much electricity is passing through. Inside the meter, there are special parts that detect and measure the flow of electricity. Depending on the type of meter, this works in different ways.
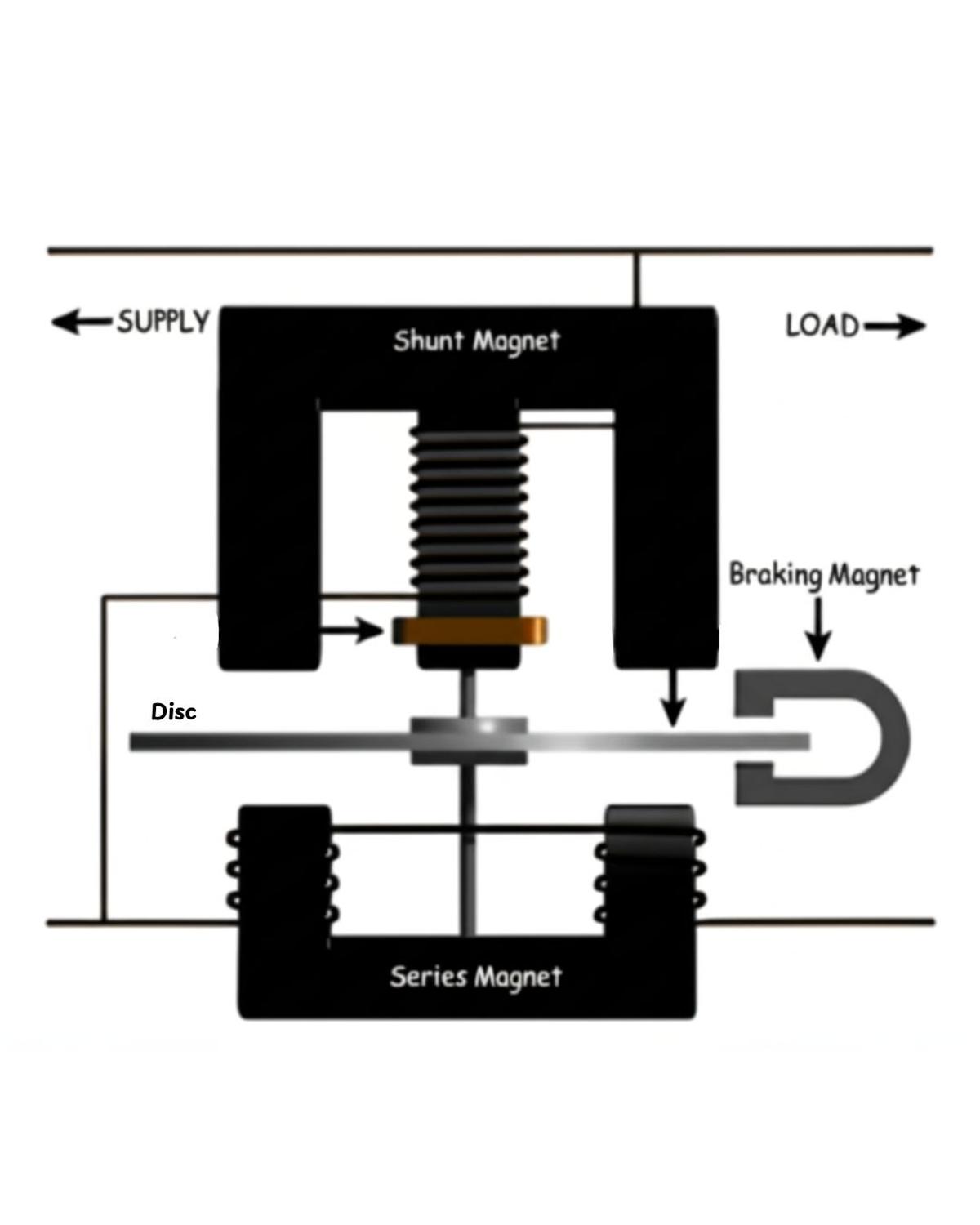
Analogue meters have a metal disc inside that spins when electricity flows. As the electricity flows, it makes a little disc inside the meter spin faster or slower depending on how much electricity is being used. The spinning turns gears connected to little dials that show how much electricity has been used. A designated official has to come and read the number on an analogue meter.
The major working principle behind an analogue electric meter is known as Electromagnetic Induction. The main parts and processes include:
-
Coils: Two coils are used in these meters: a series coil for current and a shunt coil for voltage. The current coil is connected in series with the load, while the voltage coil is connected across the voltage source.
-
Magnetic Field: A revolving aluminium disc, positioned between these coils, interacts with the magnetic field they produce.
-
Disc Rotation: The disc rotates according to the strength and phase difference of the magnetic fields. The speed of rotation is directly proportional to the power (wattage) being consumed.
-
Register: To enable the meter to record the total energy used over time, the rotating disc powers a register mechanism that counts the number of rotations.
-
Braking: To ensure an accurate reading, a permanent magnet known as an eddy current brake applies a braking force to the disc that is proportionate to its speed.
AI-generated for representational purposes.
In today’s smart world
Digital Meters, as the word suggests, are digitalised and use tiny computer chips and sensors. They measure the electric current and voltage, then calculate the energy you’ve used. The number then shows up on a digital screen, which gets updated in real time.
In smart meters, the meter sends the information automatically to the electric company using wireless signals. Most of the Indian electricity meters are smart meters now due to how efficient they are compared to the older version.
Published – June 19, 2025 10:00 am IST
